5 Consecutive Effects of Fouling on Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
- matintegrity
- Jan 6, 2023
- 3 min read
Fouling is the accumulation of unwanted deposits on the heat transfer surfaces of a shell and tube heat exchanger. These deposits can be in the form of solids or liquids and can have a number of negative effects on the heat exchanger. They can increase the resistance to heat transfer, leading to decreased efficiency and increased energy consumption. Fouling can also reduce the flow capacity of the heat exchanger and increase the pressure drop across it, both of which can lead to further increases in energy consumption. Additionally, fouling can increase the maintenance requirements of the heat exchanger, as the deposits will need to be regularly removed to restore optimal performance.
Below are the 5 consecutive effects of fouling on shell and tube heat exchangers
(1)>>>> Deposit Formation: Fouling in shell and tube heat exchangers can be caused by the formation of deposits on the heat transfer surfaces. These deposits can be in the form of solids, such as dirt, scale, or corrosion products, or they can be in the form of liquids, such as oil or grease.
One solution to prevent deposit formation is to use filtration or separation techniques to remove contaminants from the fluid before it enters the heat exchanger. This can help to reduce the amount of solids that are able to deposit on the heat transfer surfaces.
(2)>>>> Increase Resistance to Heat Transfer: As fouling deposits build up on the heat transfer surfaces, they can increase the resistance to heat transfer. This can lead to a decrease in the overall efficiency of the heat exchanger and a corresponding increase in energy consumption.
To address this issue, it may be necessary to clean the heat exchanger on a regular basis to remove fouling deposits. This can be done through the use of chemical cleaning agents or mechanical methods such as scraping or abrasive blasting.
(3)>>>> Reduce Flow Capacity: Fouling deposits can also reduce the flow capacity of the heat exchanger by partially blocking the flow of fluid through the tubes. This can lead to reduced heat transfer rates and increased pressure drop across the heat exchanger.
To restore the flow capacity of a heat exchanger that has been partially blocked by fouling deposits, it may be necessary to remove the deposits through cleaning or chemical treatment. It may also be necessary to increase the size of the heat exchanger or to use a design with a larger number of tubes to compensate for the reduced flow capacity.
(4)>>>> Increased Pressure Drop: As fouling deposits build up on the heat transfer surfaces, they can increase the pressure drop across the heat exchanger. This can lead to an increase in pumping power requirements and a corresponding increase in energy consumption.
To reduce the pressure drop across a heat exchanger that has been fouled, it may be necessary to clean the heat exchanger or to use a design with a larger number of tubes to increase the flow area.
(5)>>>> Increased Maintenance Requirements: Fouling can also increase the maintenance requirements of a heat exchanger, as the deposits will need to be removed on a regular basis to restore the heat exchanger to its optimal performance. This can be a time-consuming and costly process.
To reduce the maintenance requirements of a heat exchanger, it may be necessary to implement a preventive maintenance program that includes regular cleaning and inspections. It may also be helpful to use materials that are resistant to fouling, such as corrosion-resistant alloys or coatings, to reduce the rate at which fouling deposits build up on the heat transfer surfaces.
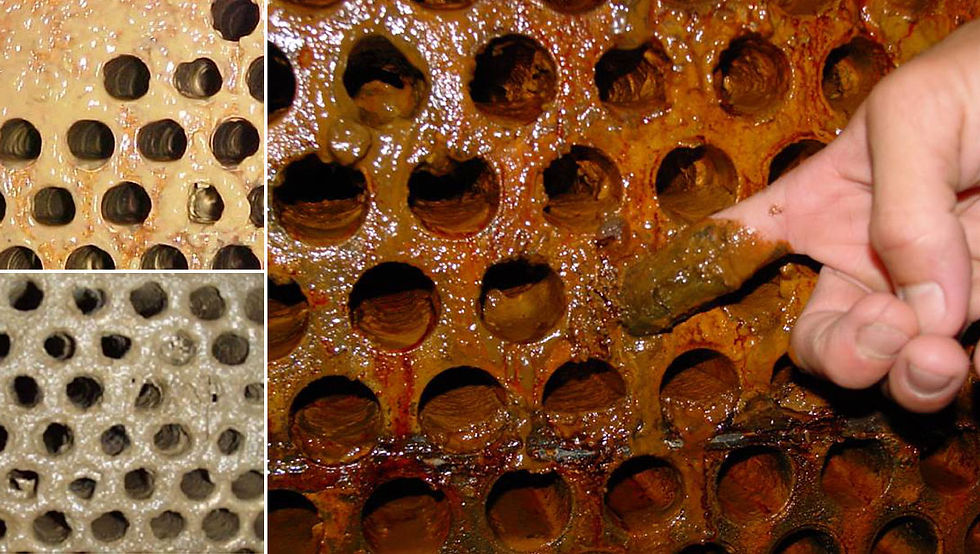
Photo credit: https://www.tcwilson.com/Images/biofilm-microbiological-mud.jpg




Comments